17 Rare Jungle Creatures Found in the World’s Most Remote Forests
The world’s most remote forests are home to some of the rarest and most fascinating creatures on Earth. Many of these animals are so elusive that they remain a mystery to scientists and nature enthusiasts alike. These creatures often thrive in habitats that are difficult for humans to access, making them even more intriguing. From the dense jungles of Southeast Asia to the tropical rainforests of South America, these animals have adapted to some of the harshest environments. Some of them are critically endangered, with their survival at risk due to habitat loss and human activity. Yet, their unique characteristics and behaviors make them vital to the ecosystems they inhabit.
This post may contain affiliate links, which helps keep this content free. Please read our disclosure for more info.
Golden Poison Dart Frog (Phyllobates terribilis)
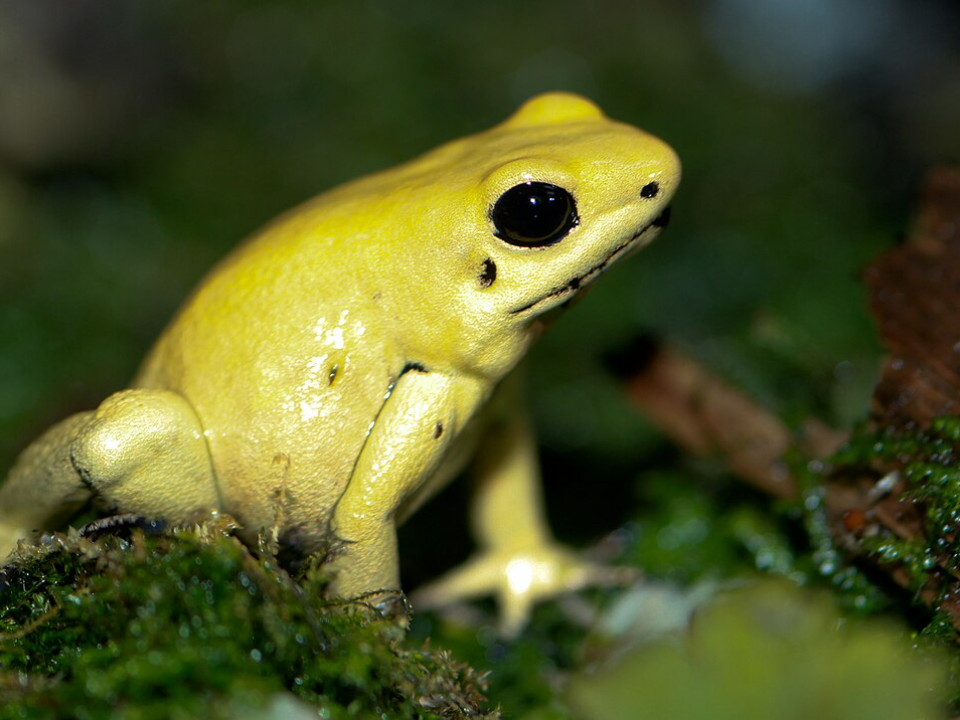

The golden poison dart frog is one of the most dangerous creatures on Earth, native to the rainforests of western Colombia. Its bright yellow color serves as a warning to predators, as it contains potent toxins that can cause severe harm. Despite its small size, this frog is capable of producing enough toxin to kill multiple humans. The chemical toxins are believed to be produced by the frog’s diet, which consists of ants and other small invertebrates that contain the necessary compounds.
This species thrives in humid, tropical environments where it can hide in the dense foliage and survive without being easily spotted. Conservation efforts are in place to protect these frogs, as their habitat is increasingly threatened by deforestation and climate change. They are an essential part of their ecosystem, controlling insect populations in the forests they inhabit. However, the golden poison dart frog remains elusive and difficult to study due to its remote habitat.
Sumatra Tiger (Panthera tigris sumatrae)
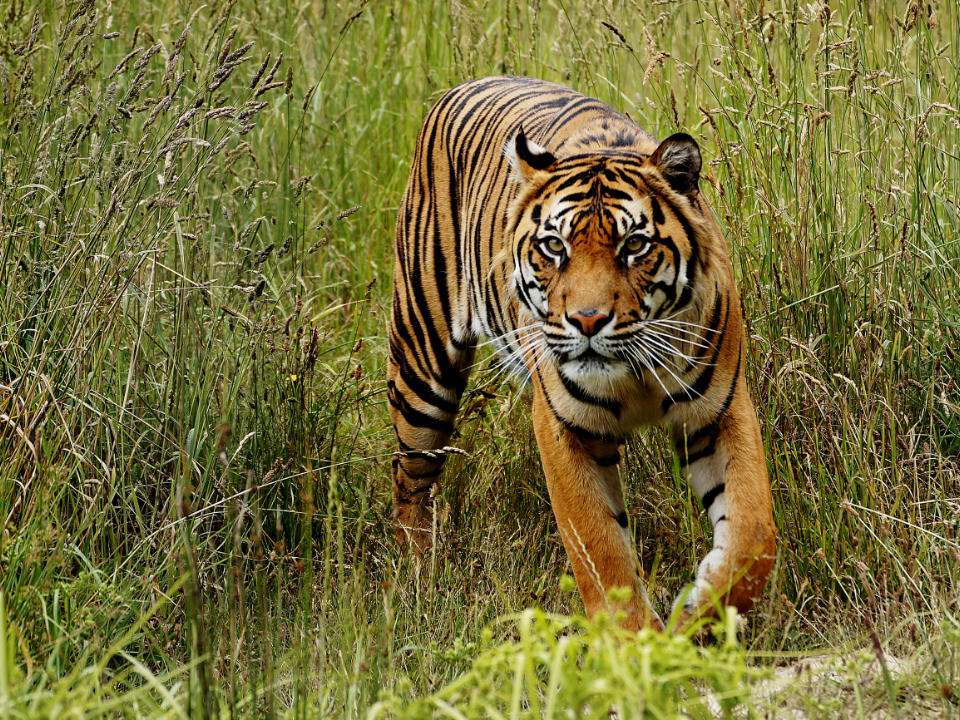

The Sumatra tiger is a subspecies of tiger found only on the Indonesian island of Sumatra. These tigers are known for their striking appearance, with bold orange coats and black stripes that help them blend into the dense jungle foliage. They are apex predators in their habitat, preying on various species, including deer, wild boar, and smaller mammals. The Sumatra tiger is smaller than other tiger subspecies, but it is equally effective as a hunter.
Sadly, the population of Sumatra tigers has been dwindling due to poaching and habitat loss caused by deforestation. These tigers are now critically endangered, and efforts to protect them have been ramped up in recent years. Protected areas on the island have been established to provide a safe environment for the tigers to thrive. However, illegal logging and human-wildlife conflict remain significant challenges to their long-term survival.
Binturong (Arctictis binturong)
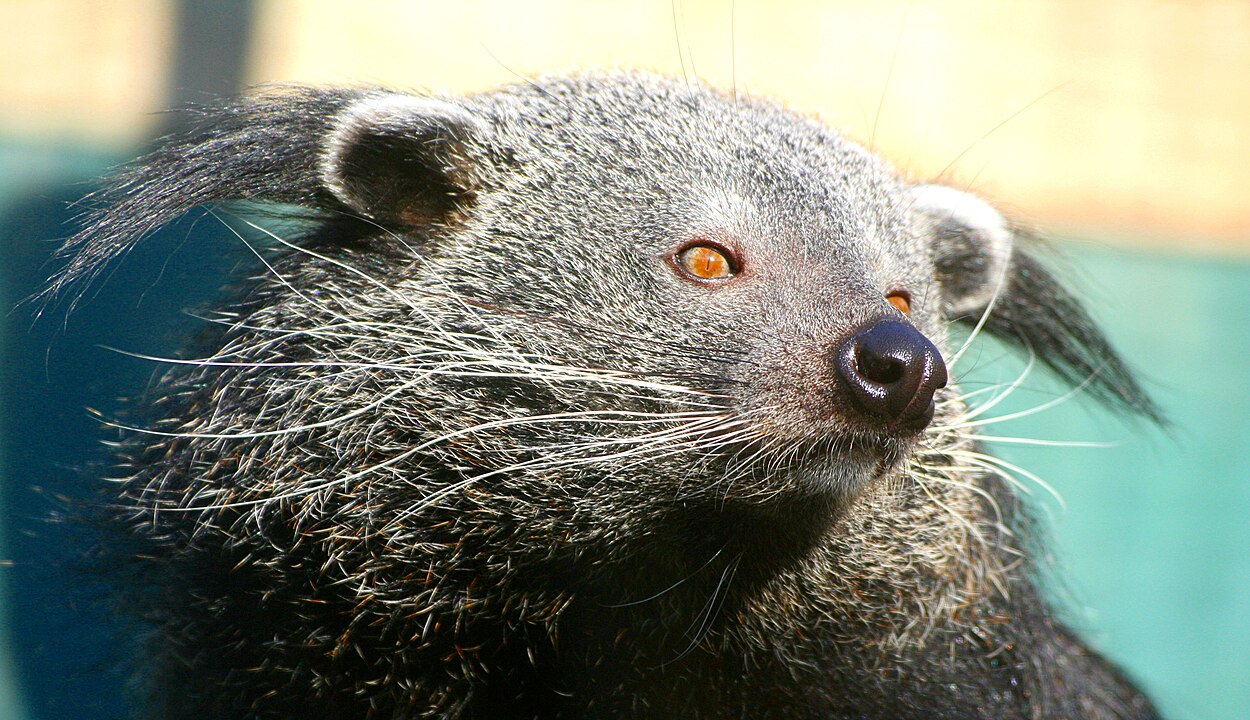

The binturong, also known as the bearcat, is a nocturnal mammal found in the forests of Southeast Asia. It has a distinctive appearance, with a thick, black coat and a prehensile tail that allows it to easily navigate the trees. Binturongs are omnivores, feeding on a variety of fruits, small animals, and even insects. They are known for their musky scent, which is often described as smelling like buttered popcorn, and it is used for communication.
This unique creature is arboreal and spends most of its life in the tree canopy. However, it is becoming increasingly threatened due to habitat destruction and poaching. The binturong is a vital part of its ecosystem, helping to control insect and small vertebrate populations. Conservation programs are focused on protecting the rainforests of Southeast Asia, where the binturong plays an important ecological role.
Okapi (Okapia johnstoni)
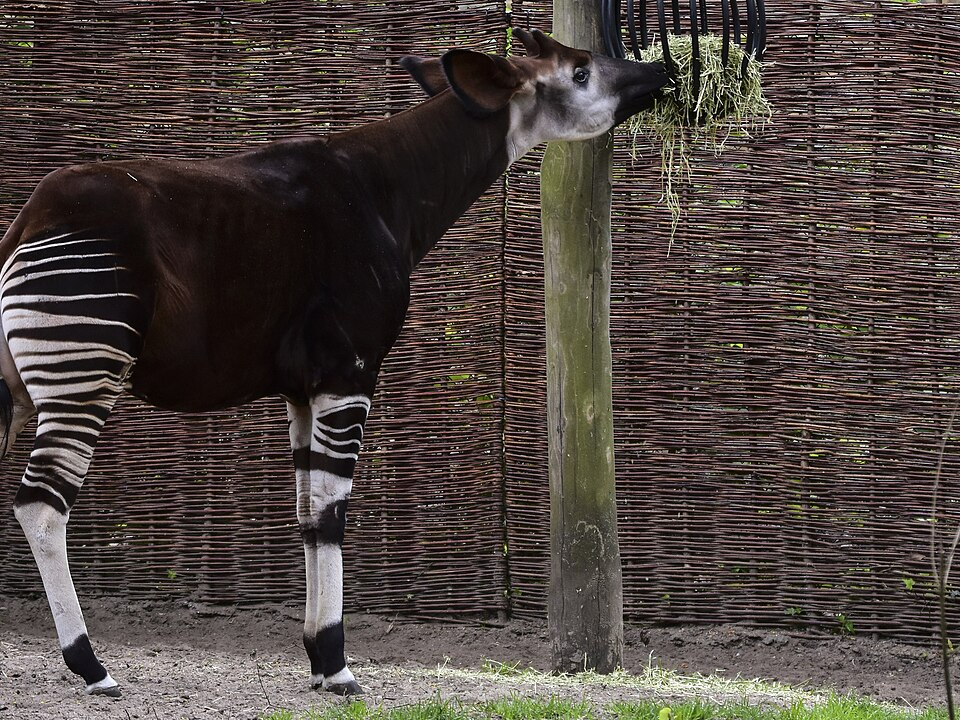
The okapi is an elusive herbivorous mammal found in the dense rainforests of the Democratic Republic of Congo. With its striking appearance, the okapi has a body that resembles a horse but features the dark coat and zebra-like stripes on its legs. The okapi is closely related to the giraffe, though it is much smaller in size. It feeds on leaves, fruits, and grasses, using its long tongue to grasp vegetation.
Okapis are solitary animals, and their shy, nocturnal nature makes them difficult to study in the wild. As a result, they were not discovered by scientists until the early 20th century. The primary threat to their survival is deforestation, as large portions of their habitat are being destroyed for agriculture and logging. Efforts to protect the okapi are ongoing, with several wildlife reserves established to safeguard its rainforest home.
Kakapo (Strigops habroptilus)
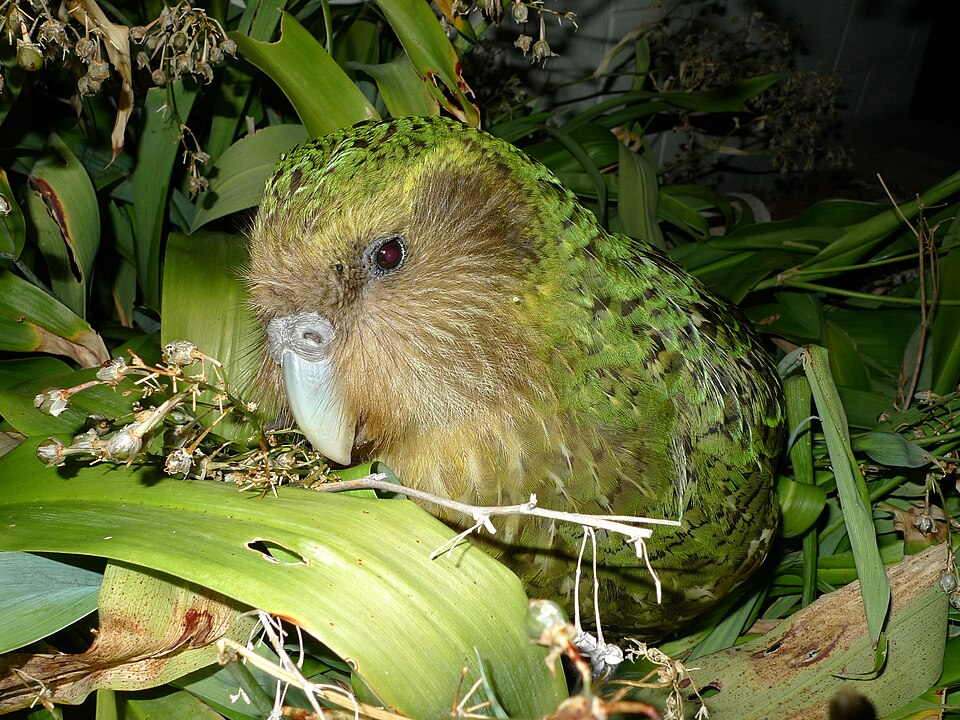

The kakapo is a flightless parrot native to New Zealand, renowned for its large size and nocturnal habits. Its green plumage provides excellent camouflage in the dense forest undergrowth. Unlike most parrots, the kakapo is nocturnal and spends much of its time on the ground, foraging for food. The bird is herbivorous, feeding on native plants, seeds, and fruits.
Once widely distributed across New Zealand, the kakapo now faces a significant risk of extinction due to introduced predators like rats and stoats. Conservationists have worked tirelessly to establish predator-free islands where the kakapo can live safely and breed. These efforts have led to a slow but steady increase in the kakapo population, though it remains critically endangered. The kakapo is now one of the rarest birds in the world, with fewer than 250 individuals remaining.
Greater Bilby (Macrotis lagotis)
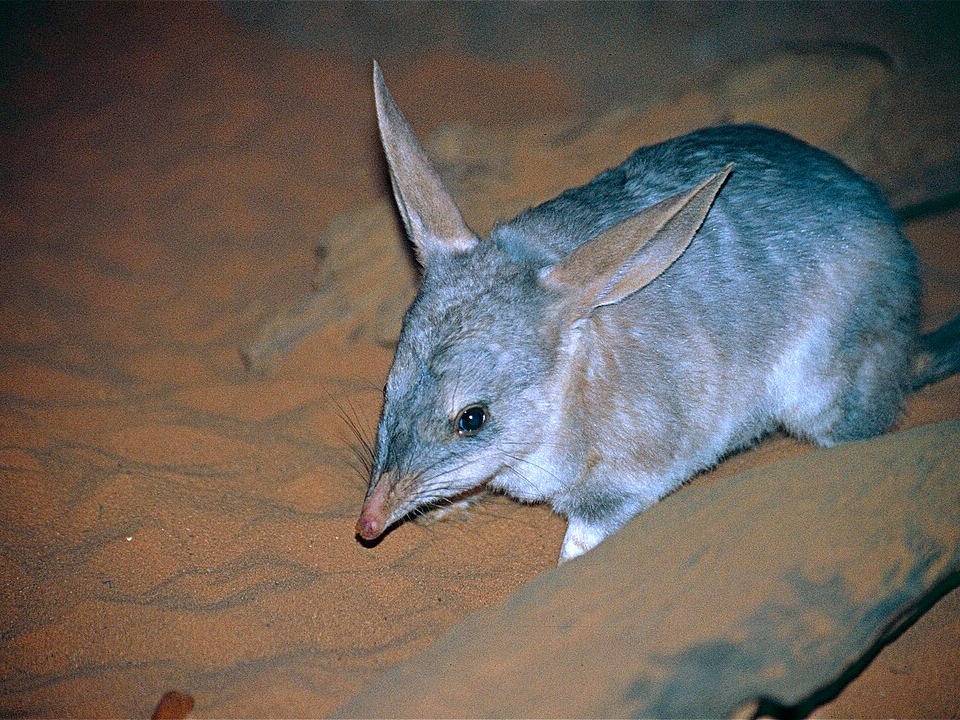

The greater bilby is a nocturnal marsupial that once thrived across much of Australia. Known for its large ears and long, pointed snout, the bilby is highly adapted to desert and woodland environments. It uses its strong hind legs to dig burrows where it sleeps during the day and hunts for food at night. The bilby feeds on a variety of small insects, seeds, and roots.
Once widespread, the bilby’s population has drastically declined due to habitat destruction, introduced predators, and competition with other species. Conservation efforts have included breeding programs and the creation of protected areas where bilbies can live without the threat of predators. The greater bilby remains a symbol of wildlife preservation in Australia, and efforts continue to restore its populations to the wild.
Glass Frog (Centrolenidae family)
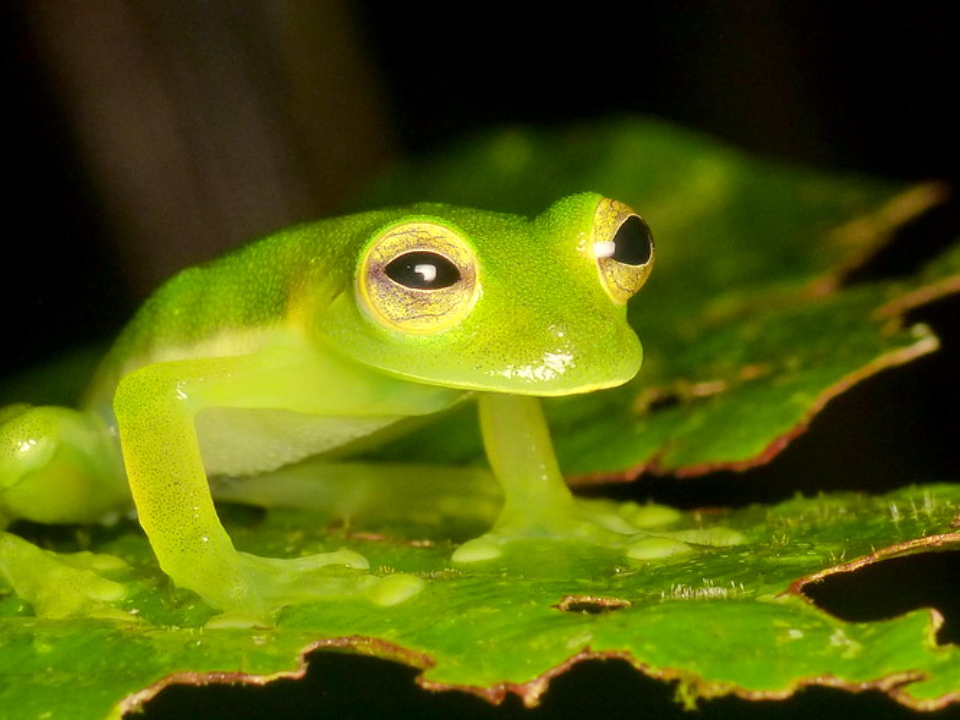

Glass frogs are known for their translucent undersides, which give them their name. Found in the tropical rainforests of Central and South America, these frogs are small in size and often hide under leaves to avoid predators. The transparency of their bellies allows their internal organs to be seen, a feature that fascinates both researchers and nature enthusiasts. Glass frogs primarily feed on small insects and arthropods, using their long tongues to capture prey.
Despite their fascinating appearance, glass frogs are vulnerable to deforestation and habitat destruction. Their populations are declining due to the loss of their rainforest homes, and many species are now classified as endangered. Conservation efforts are aimed at protecting the ecosystems that these frogs depend on, as they play an important role in maintaining insect populations in their habitats. The glass frog’s unique features make it an important species for scientific study.
Spiny Anteater (Zyzomys)
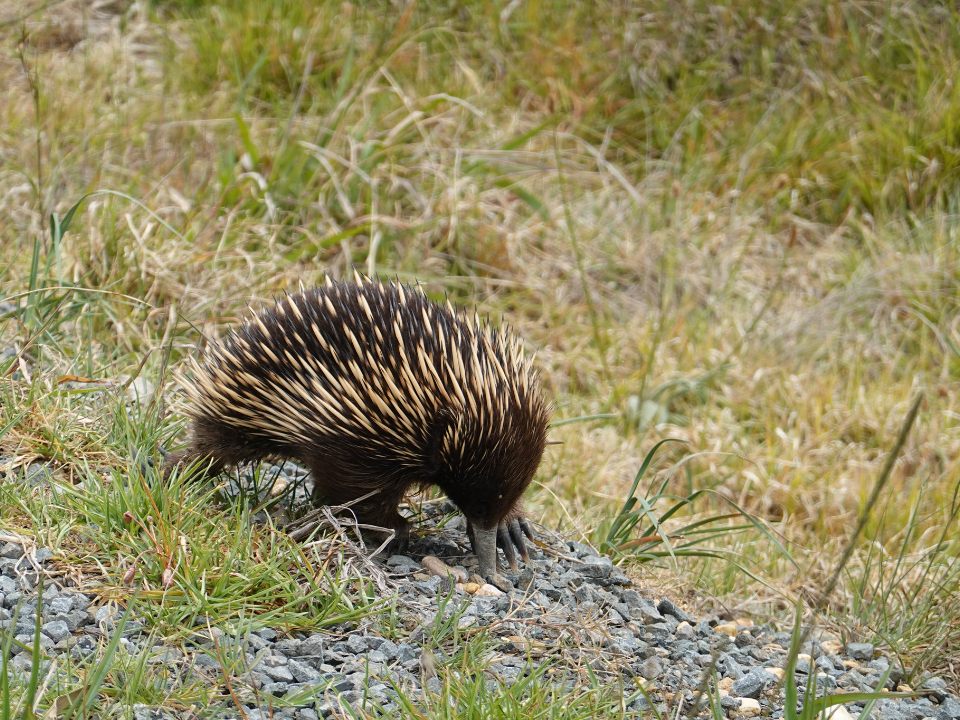

The spiny anteater, or echidna, is a fascinating monotreme found in the remote forests of Australia. This egg-laying mammal has spines covering its back, which help protect it from predators. Its diet primarily consists of ants and termites, which it uncovers with its strong claws. Despite its tough appearance, the echidna is a shy and solitary animal, spending most of its time burrowed in the earth.
As an ancient species, the echidna is one of the few surviving monotremes, which are mammals that lay eggs. However, habitat loss and climate change are affecting its population, especially in certain parts of Australia. Conservation measures are in place to protect this unique creature, and efforts focus on maintaining its habitat and monitoring its populations. The spiny anteater plays an important role in controlling insect populations in its environment.
Red Uakari (Cacajao calvus)
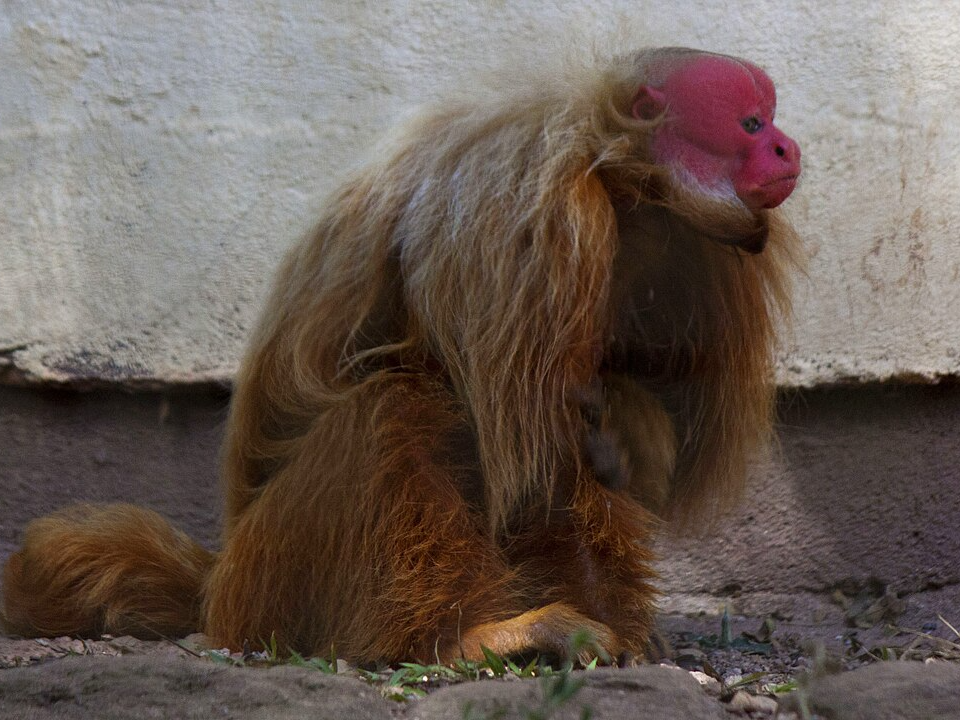

The red uakari is a striking monkey native to the Amazon rainforest in South America. Known for its bright red face and white fur, it is one of the most visually distinctive primates in the world. These monkeys live in the dense forests of the Amazon basin, where they primarily feed on fruits, seeds, and leaves. They are social animals, often found in groups, and are known for their vocalizations and playful behavior.
The red uakari’s habitat is under threat from deforestation and illegal hunting. Their population has significantly declined, and they are now considered vulnerable. Conservation programs aim to protect the rainforest and create safe environments for these primates. Protecting the red uakari’s habitat is essential for maintaining the balance of the ecosystem they depend on.
Malayan Pangolin (Manis javanica)
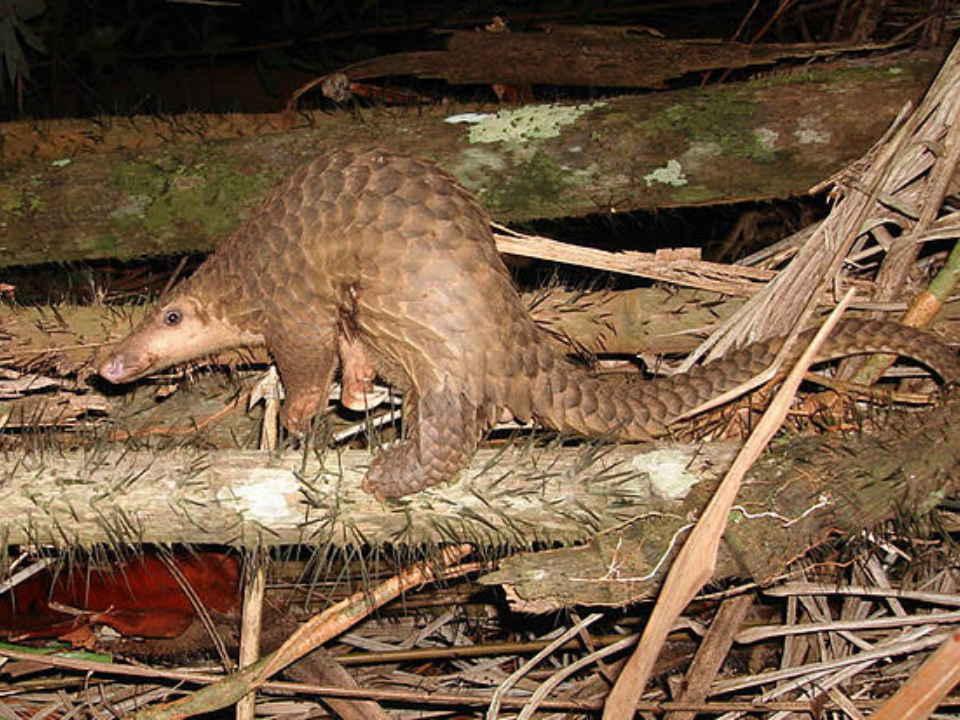

The Malayan pangolin is a nocturnal mammal known for its scaly body and unique defense mechanism. Native to the rainforests of Southeast Asia, it rolls into a tight ball when threatened, using its sharp scales for protection. Pangolins are insectivores, feeding primarily on ants and termites, which they extract with their long, sticky tongues.
Pangolins, including the Malayan species, are critically endangered due to poaching for their meat and scales, which are highly prized in traditional medicine. Conservation efforts are focused on cracking down on illegal trade and protecting their natural habitat. These creatures are vital for controlling insect populations in their ecosystems. Efforts to conserve the Malayan pangolin include stricter laws and increased public awareness.
Yellow-eyed Penguin (Megadyptes antipodes)
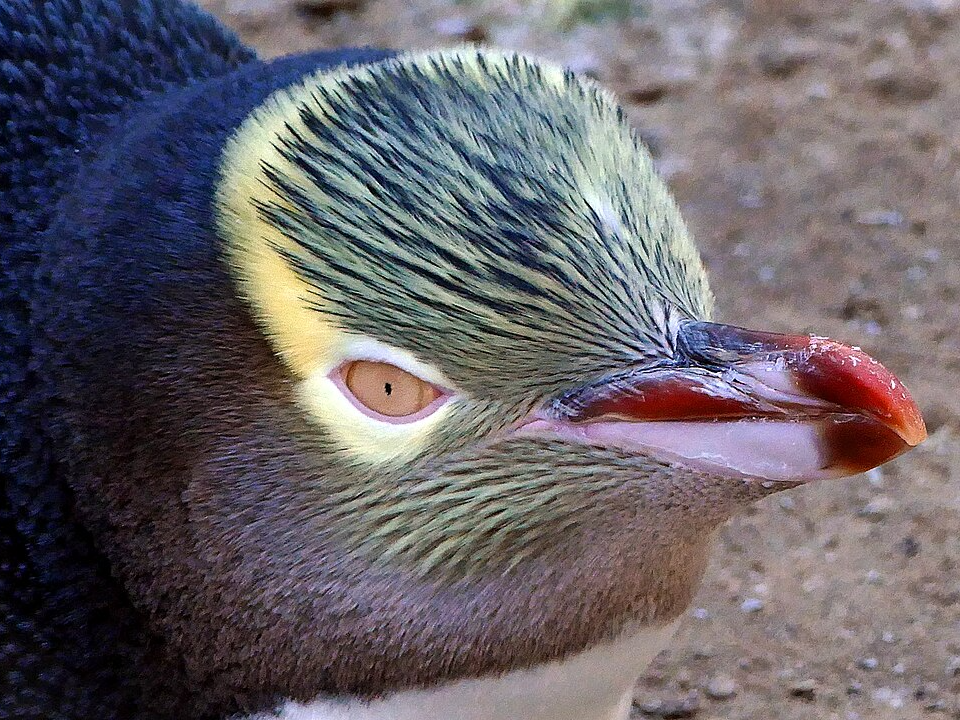

The yellow-eyed penguin, native to the forests of New Zealand, is one of the rarest and most threatened penguin species in the world. Known for its pale yellow eyes and distinctive pale yellow-feathered head, this penguin is largely terrestrial, living in dense forests along the coast. It is a solitary bird, often found alone or in small groups.
The yellow-eyed penguin’s population has been steadily declining due to habitat destruction, introduced predators, and disease. Today, fewer than 200 individuals remain in the wild, making it critically endangered. Efforts to protect the species focus on controlling predators, restoring habitats, and supporting breeding programs. These penguins are a vital part of New Zealand’s unique biodiversity and play an important role in the local ecosystem.
Sumatran Rhinoceros (Dicerorhinus sumatrensis)
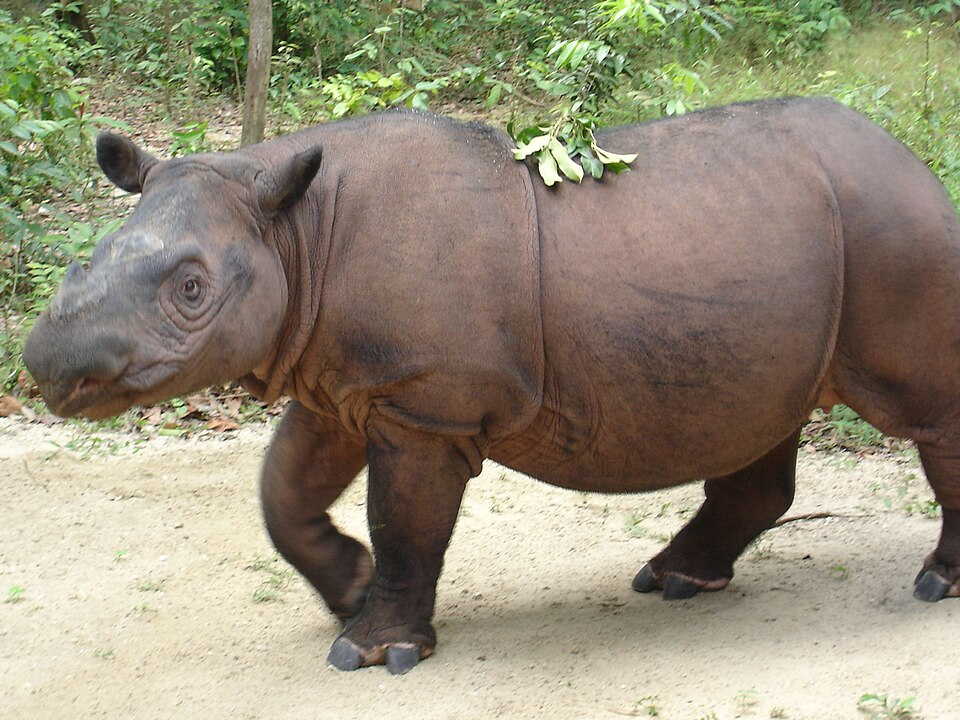

The Sumatran rhinoceros is one of the smallest rhino species and is found in the rainforests of Borneo and Sumatra. These rhinos are distinguished by their thick, dark skin and two horns, the larger of which is located on their nose. Despite being herbivores, they play an important role in maintaining the health of the forest by dispersing seeds and promoting the growth of various plant species.
The Sumatran rhinoceros is critically endangered, with fewer than 80 individuals left in the wild. Habitat loss due to deforestation and poaching for their horns are the primary threats to their survival. Conservationists are working to protect the remaining population and prevent the species from disappearing. Conservation programs focus on habitat preservation, anti-poaching measures, and breeding initiatives.
Philippine Tarsier (Carlito syrichta)
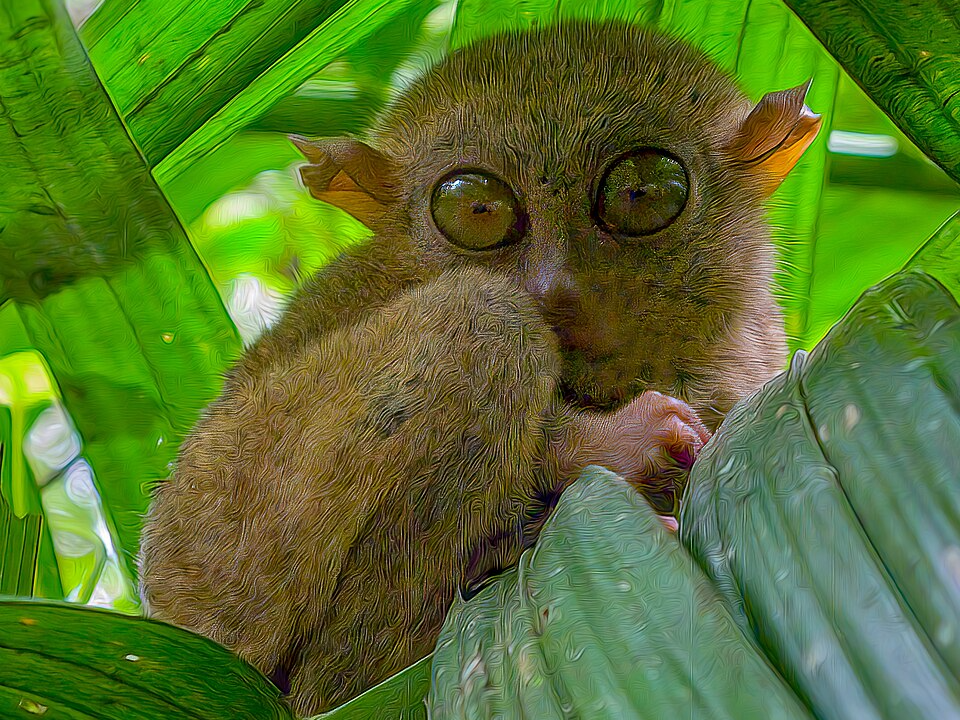

The Philippine tarsier is a small, nocturnal primate found in the forests of the Philippines. It is known for its large eyes, which are adapted to its nocturnal lifestyle, and its small, round face. The tarsier feeds on insects, birds, and small mammals, using its strong hind legs to leap between trees.
This species is endangered due to habitat loss and hunting. The tarsier is often seen as a symbol of conservation in the Philippines, and efforts are being made to protect its forest homes. Sanctuaries have been established to protect tarsier populations, and eco-tourism has become a way to raise awareness about the species. With continued protection, the Philippine tarsier has a chance to recover.
Pygmy Marmoset (Cebuella pygmaea)
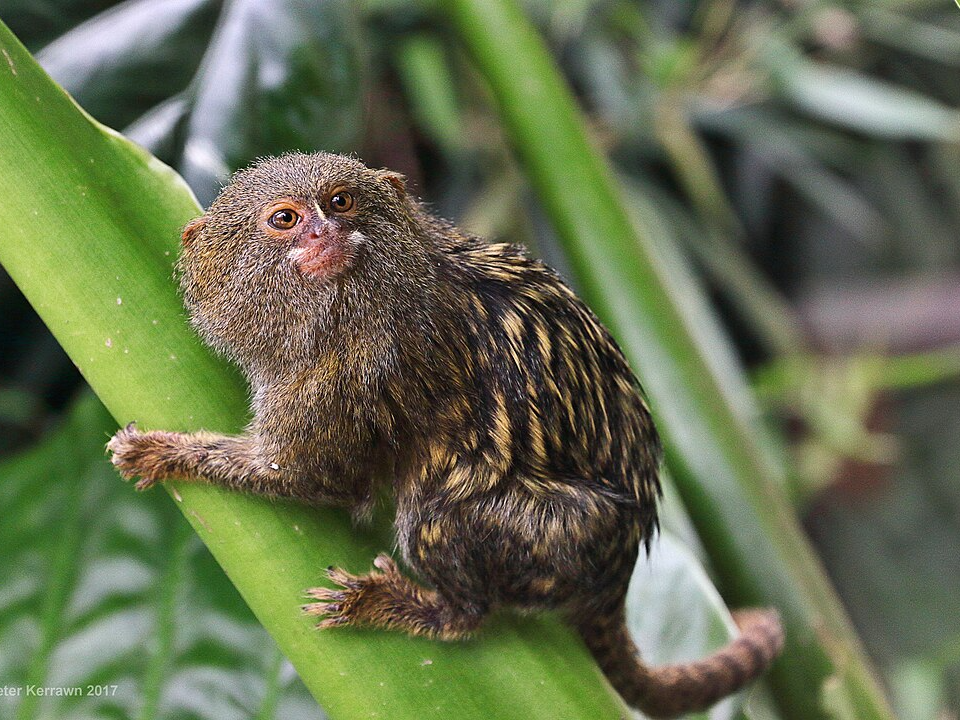

The pygmy marmoset is the smallest monkey in the world, weighing only about 100 grams. It is found in the rainforests of South America, particularly in the Amazon basin. These tiny primates have adapted to life in the dense underbrush, where they use their sharp claws to cling to tree trunks and vines. They feed primarily on insects, fruits, and tree sap.
Despite their small size, pygmy marmosets play a vital role in their ecosystem by helping to disperse seeds and pollens. However, their population is threatened by habitat destruction due to deforestation. They are also frequently captured for the illegal pet trade. Protecting their forest habitats is key to ensuring the survival of these unique creatures.
Bornean Orangutan (Pongo pygmaeus)
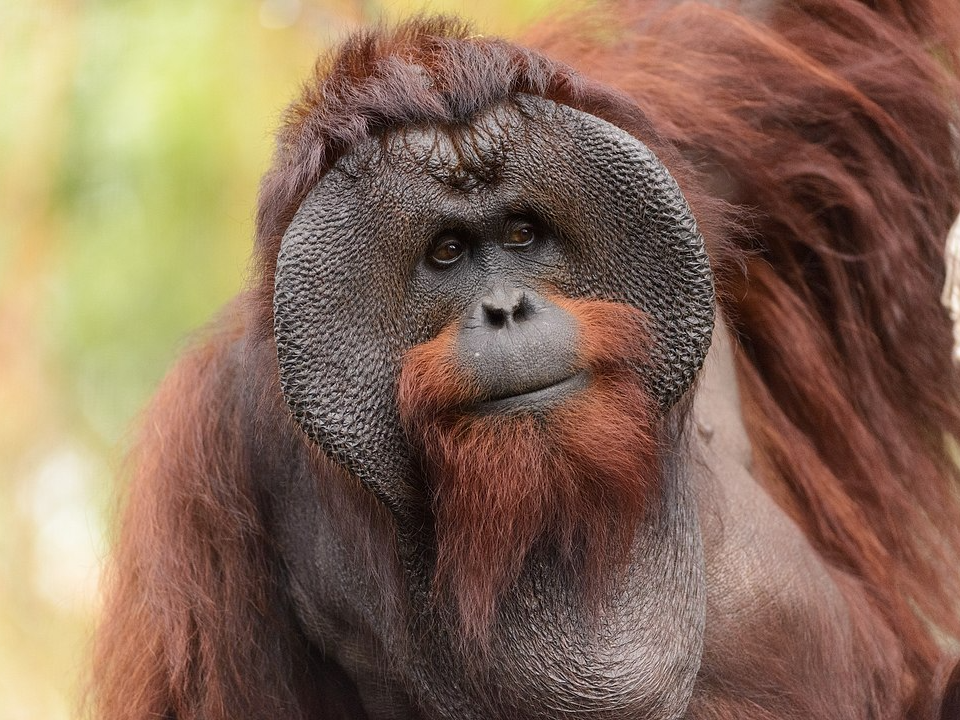

The Bornean orangutan is an intelligent and critically endangered primate found in the rainforests of Borneo. These orangutans have reddish-brown fur and spend most of their time in trees, where they build nests to sleep in. They are omnivorous, feeding on fruit, leaves, and insects.
The Bornean orangutan is critically endangered due to habitat loss caused by logging, palm oil plantations, and poaching. With fewer than 14,000 individuals remaining, they are at serious risk of extinction. Conservation programs are working to preserve their forest habitat and reduce human-wildlife conflict. Protecting the Bornean orangutan is vital to maintaining the balance of the rainforest ecosystem.
Amazon River Dolphin (Inia geoffrensis)
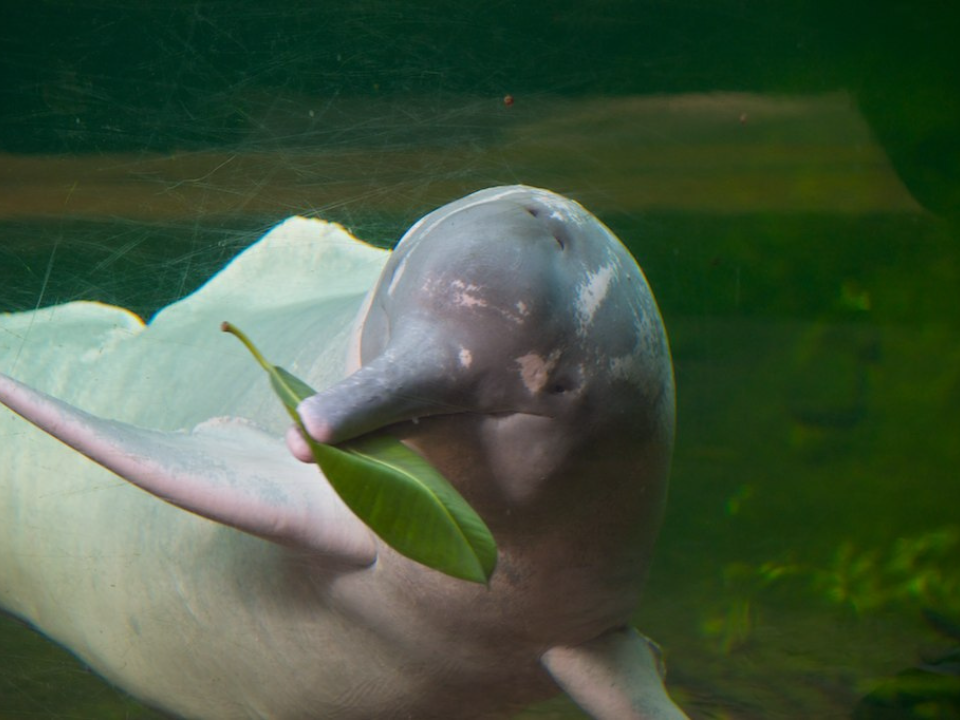

The Amazon river dolphin, also known as the pink river dolphin, is a freshwater species native to the Amazon River and its tributaries. These dolphins are notable for their distinctive pink color, which intensifies with age. They have a highly flexible neck and can rotate their heads almost 90 degrees, allowing them to navigate through the dense waters of the rainforest.
The Amazon river dolphin is threatened by habitat loss, water pollution, and illegal hunting. Conservation efforts focus on protecting the Amazon River’s ecosystem and raising awareness about the importance of these dolphins. As apex predators in their environment, they play a key role in maintaining the health of the river’s ecosystem.
Vietnamese Mossy Frog (Theloderma corticale)
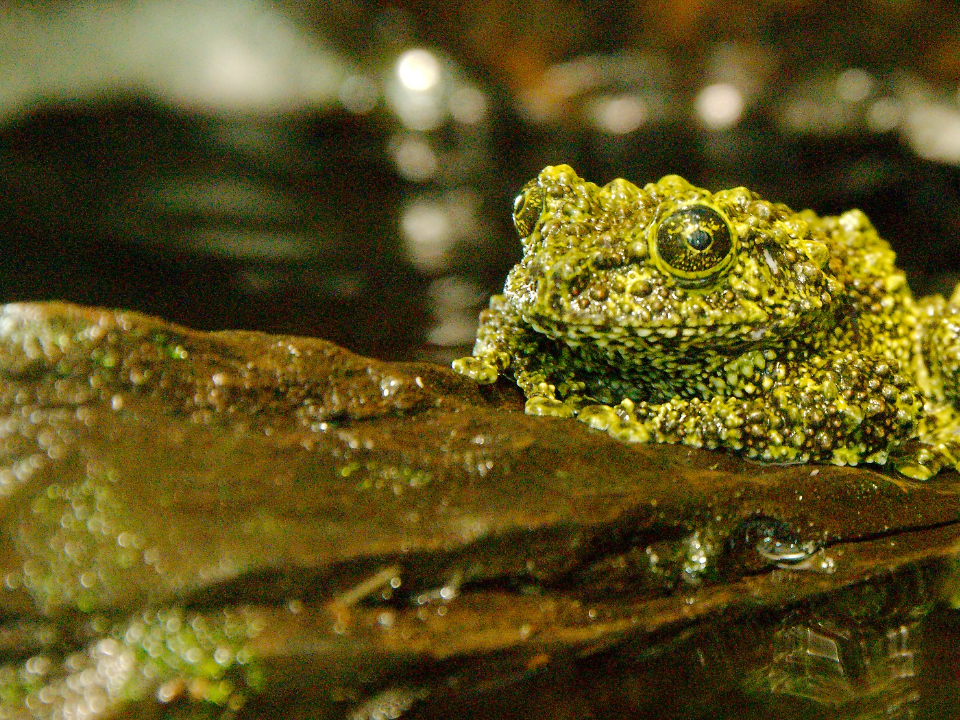

The Vietnamese mossy frog is a unique amphibian that blends in perfectly with its environment. Native to the forests of Vietnam, this frog has green, lichen-like markings on its body that help it remain hidden from predators. It lives in humid, tropical areas, often found perched on tree branches or rocks near streams.
Although its camouflage is impressive, the Vietnamese mossy frog is under threat due to habitat loss and the pet trade. It is a challenging species to study, as it thrives in remote and inaccessible regions. Efforts are underway to protect its habitat and prevent further population decline. This frog is an important part of its ecosystem, controlling insect populations.
This article originally appeared on Avocadu.
