12 Fascinating Animals You Won’t Believe Actually Exist
From the depths of the ocean to remote corners of the world, nature is home to some truly extraordinary creatures. These animals boast appearances and behaviors that defy the imagination, making them hard to believe, even though they are very real. Whether it’s their unusual physical traits or remarkable survival skills, these creatures continue to captivate and surprise us. Get ready to discover some of the most bizarre and fascinating species that nature has to offer.
This post may contain affiliate links, which helps keep this content free. Please read our disclosure for more info.
Axolotl
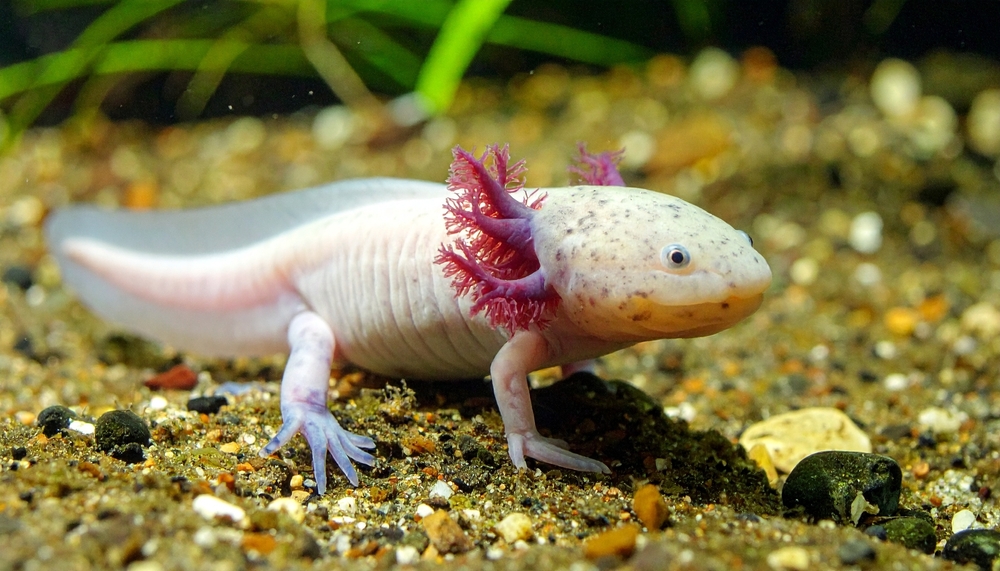

The axolotl is an aquatic salamander native to lakes in Mexico, but what truly sets it apart is its ability to retain its juvenile features throughout its life. Unlike most amphibians, which undergo metamorphosis, the axolotl stays in its larval form, retaining external gills and an aquatic lifestyle. This fascinating feature, known as “neoteny,” means that the axolotl never fully matures into a land-dwelling adult like other salamanders.
Beyond its strange appearance, the axolotl has extraordinary regenerative abilities. It can regenerate entire limbs, parts of its spinal cord, heart, and even parts of its brain, a unique trait that has drawn the attention of scientists worldwide. While these creatures are captivating, they are critically endangered in the wild due to habitat loss, making them all the more precious.
Platypus
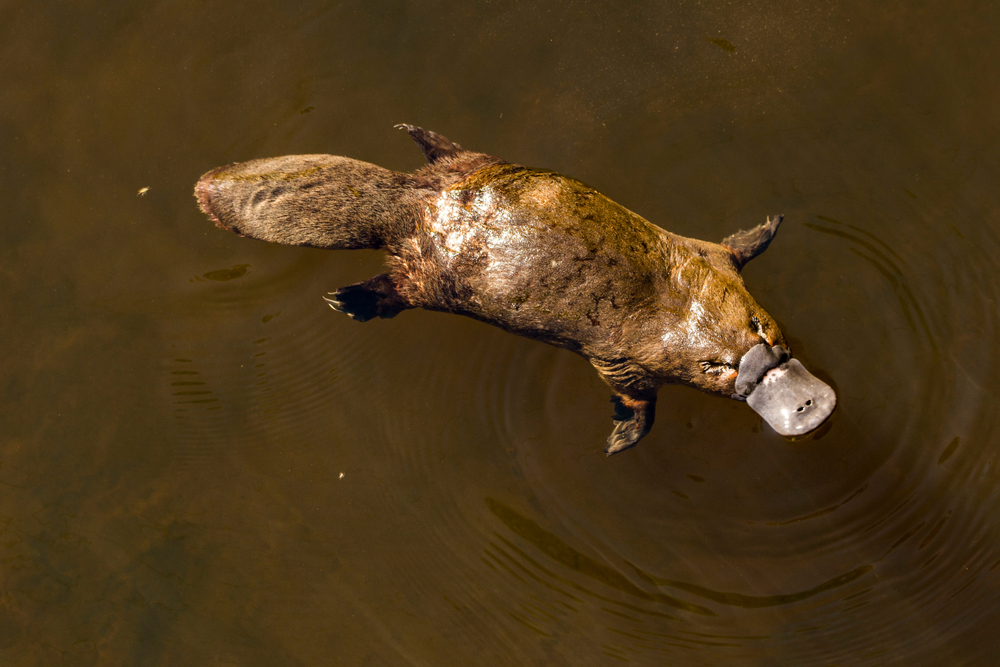

The platypus is a one-of-a-kind mammal that looks like it was designed by combining different animals. It has the webbed feet of an otter, a bill like a duck, and the tail of a beaver. Native to Australia, it is one of only five species of monotremes, mammals that lay eggs. Its ability to thrive in water, combined with its mammalian traits, makes the platypus both fascinating and puzzling.
What further sets the platypus apart is its ability to detect electric fields in the water. Using electroreception, it can hunt small prey like insects and crustaceans underwater with its eyes, ears, and nose closed. This remarkable trait, along with its egg-laying nature, challenges the traditional boundaries of mammalian biology and makes the platypus a true marvel of the natural world.
Naked Mole Rat
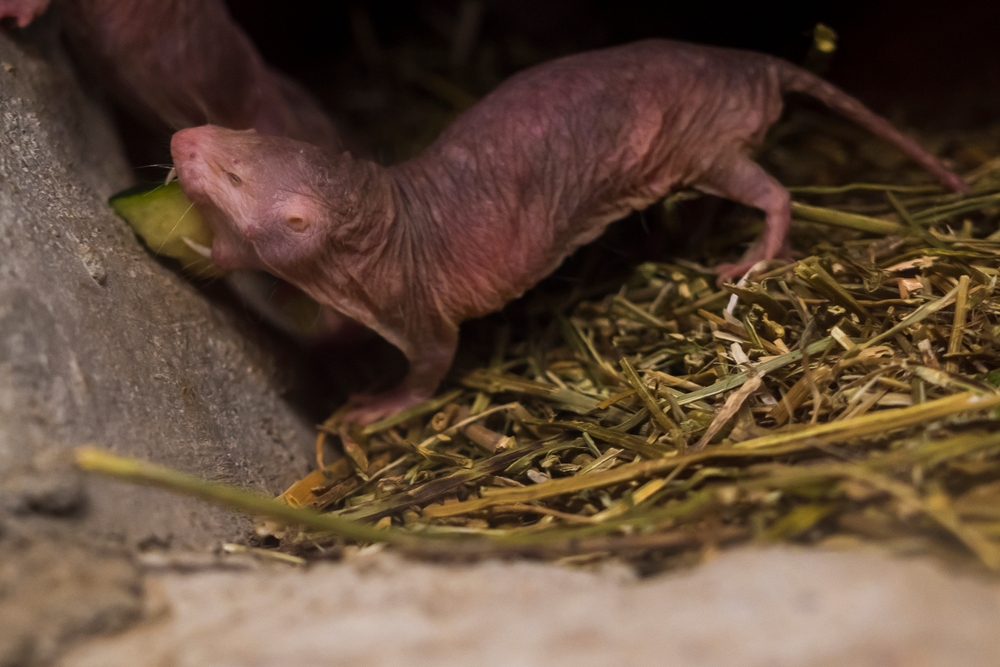

The naked mole rat is a highly social, underground-dwelling rodent found in East Africa. What makes these creatures extraordinary is their hairless, wrinkled appearance and their eusocial structure, which resembles that of ants or bees. These mole rats live in colonies where only one female, the queen, breeds, while the rest of the colony serves as workers or soldiers, much like in insect colonies.
In addition to their social organization, naked mole rats exhibit some remarkable biological traits. They are resistant to cancer and show an unusual ability to live for extended periods without oxygen, thriving in the low-oxygen environments of underground tunnels. This makes them not only bizarre in appearance but also extraordinary in terms of their unique survival mechanisms.
Sea Slug (Elysia chlorotica)
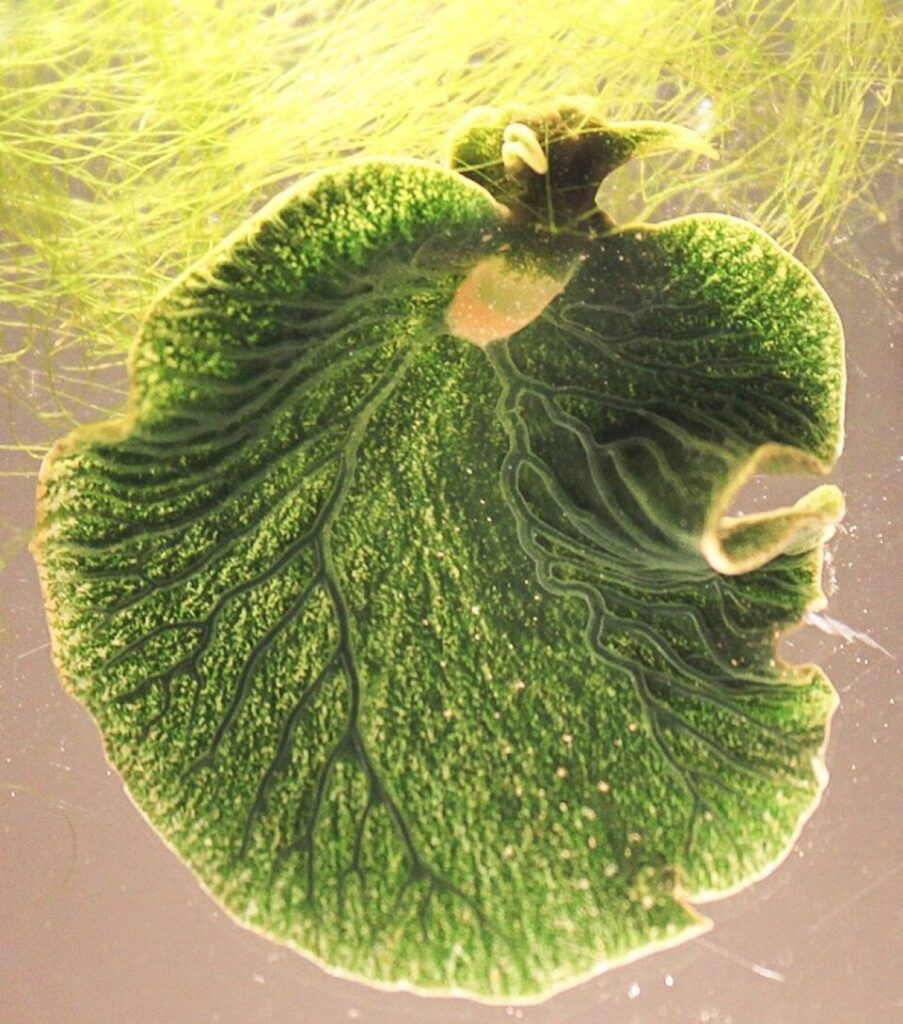

The Elysia chlorotica, or Eastern Emerald Elysia, is a type of sea slug known for its striking green color. This fascinating creature has the incredible ability to photosynthesize, much like plants. It achieves this by consuming algae and incorporating the algae’s chloroplasts into its cells. This process, called “kleptoplasty,” allows the sea slug to use sunlight as an energy source, similar to how plants produce food.
The ability to photosynthesize is rare among animals, and the Elysia chlorotica is one of the few creatures on Earth that can do so. Its vibrant green appearance comes from the algae it eats, making it a living example of nature’s ability to adapt and create unique survival strategies. This remarkable sea slug continues to fascinate biologists who are studying the potential applications of its unique abilities.
Aye-Aye
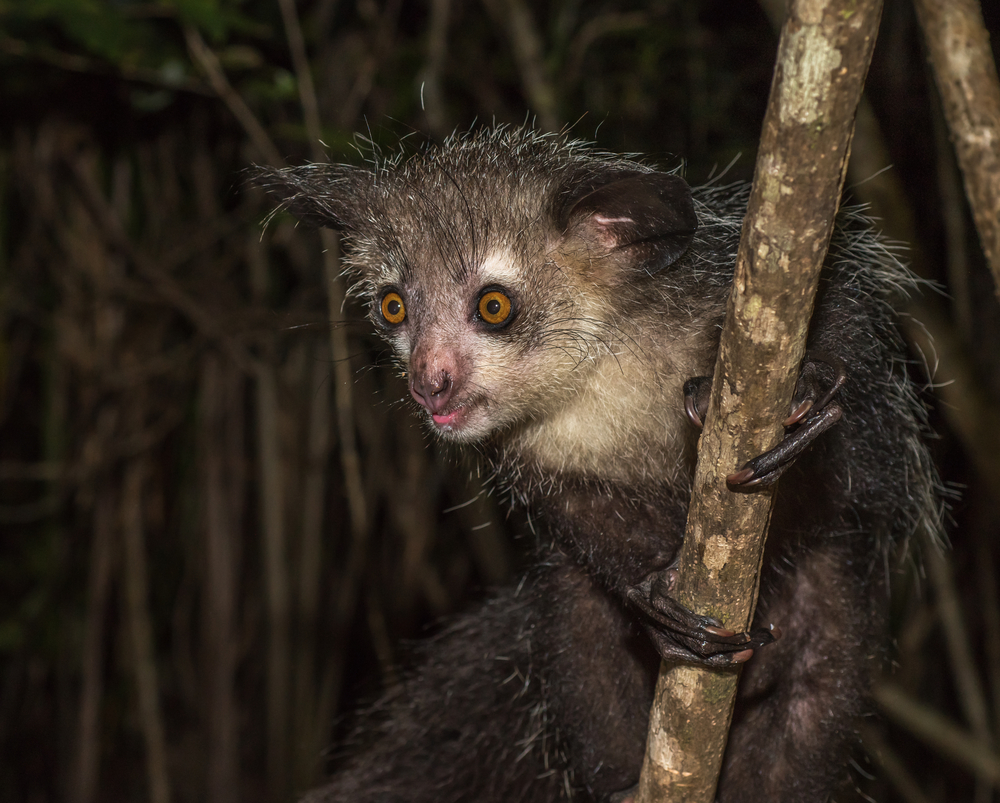

The aye-aye is a type of lemur native to Madagascar, and it is one of the most unusual primates in the world. With its large eyes and bushy tail, the aye-aye might look like something from a fantasy novel. However, it is its long, thin middle finger that sets this nocturnal animal apart. The aye-aye uses this finger to tap on trees to find hollow spaces, then extracts insects from the bark or wood by using the finger to fish them out.
While its appearance and behavior are fascinating, the aye-aye is often misunderstood and feared by local populations. Its reputation as an omen of death has led to its persecution in the past. Despite this, the aye-aye plays an important role in its ecosystem by helping to control insect populations, and it continues to captivate those who study the bizarre creatures of Madagascar.
Glass Frog
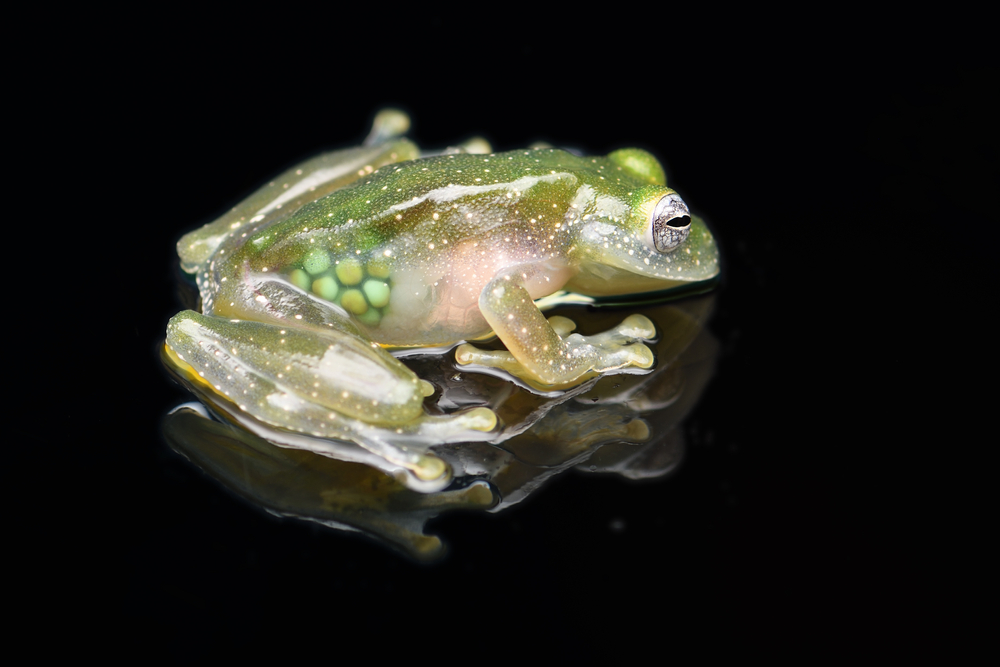

The glass frog, found in the rainforests of Central and South America, is named for its translucent skin. This frog’s underbelly is so clear that you can see its internal organs, including the heart and intestines, through the skin. While its green back helps it blend in with its environment, the transparency of its underside is a striking adaptation that protects it from predators, as its organs become nearly invisible in the dim light of the forest floor.
Glass frogs are small and mostly nocturnal, making them elusive creatures to spot. Their unique appearance has made them a subject of fascination, and scientists continue to study the mechanisms behind their transparency. These frogs are an example of how nature can create defense strategies that are as beautiful as they are effective.
Goblin Shark
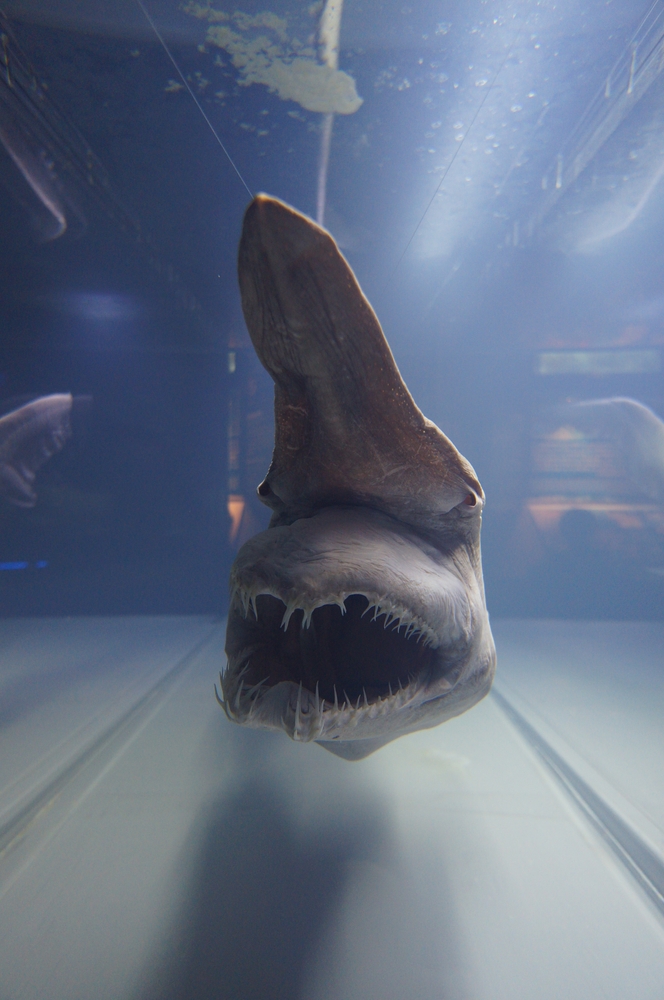

The goblin shark is a deep-sea species that looks like something out of a science fiction movie. With its long, flat snout and protruding, sharp teeth, this “living fossil” has been around for millions of years with minimal change. Its unusual appearance is complemented by a highly specialized feeding mechanism where its jaw can extend forward to catch prey, making it one of the most bizarre sharks in the ocean.
Goblin sharks are rarely seen by humans due to their preference for deep ocean habitats, but when they are encountered, their strange, almost alien features never fail to astonish. Their unique adaptation for catching prey in the darkness of the deep sea helps them thrive in an environment where few other predators can survive.
Quokka
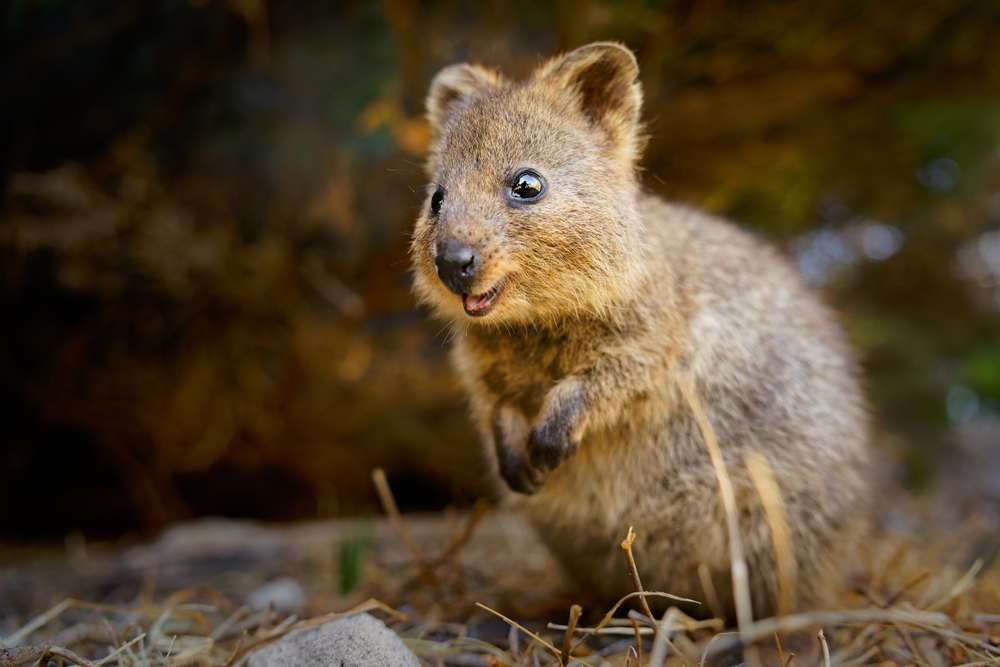

The quokka is a small marsupial native to Australia, often referred to as the “world’s happiest animal” due to its endearing, seemingly smiling face. These creatures are herbivores and are known for their friendly demeanor, often gently interacting with humans. Quokkas primarily live on small islands off the coast of Western Australia, where they are protected from many of the threats that endanger their populations on the mainland.
Despite their popularity on social media, quokkas are in danger due to habitat loss and introduced predators. However, their charming appearance and calm nature have made them a symbol of joy and have earned them a dedicated following among wildlife enthusiasts. Their “smile” is a product of their facial structure, but it has earned them fame and affection worldwide.
Yeti Crab
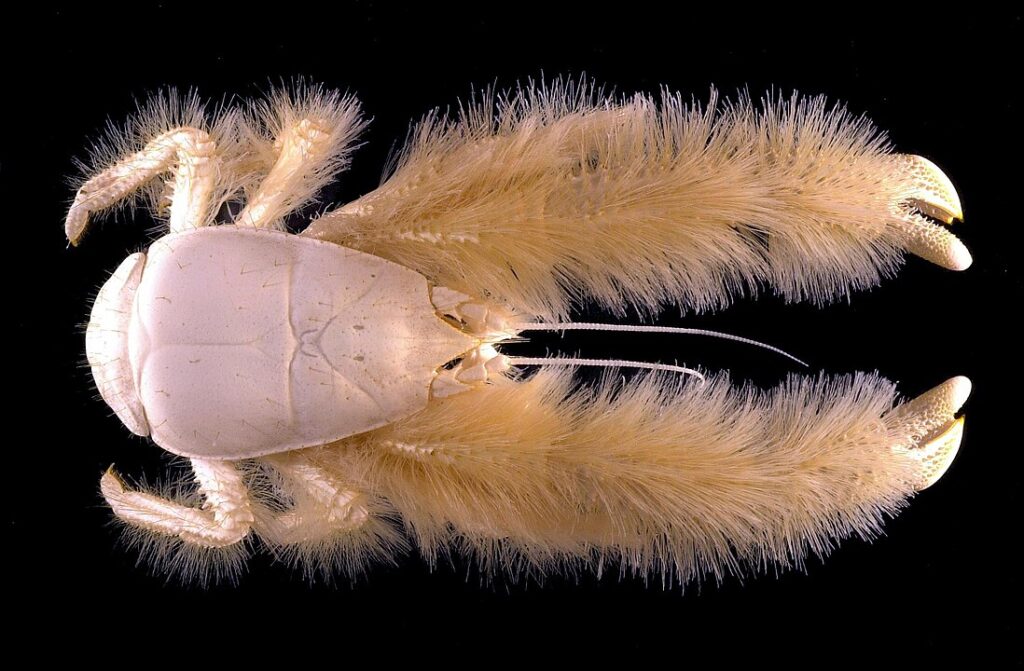

The yeti crab, discovered in the South Pacific Ocean in 2005, is named for its furry pincers, which look as though they belong to a mythical creature. These pincers are covered in yellow bacteria that the crab uses to detoxify the water around hydrothermal vents. The yeti crab is a deep-sea species that thrives in areas with extreme conditions, where other marine life struggles to survive.
This unusual adaptation allows the yeti crab to live in an environment that would be inhospitable to most creatures. Its discovery expanded our understanding of life in extreme environments, showing that creatures can thrive even in conditions of extreme heat and low oxygen levels.
Solenodon
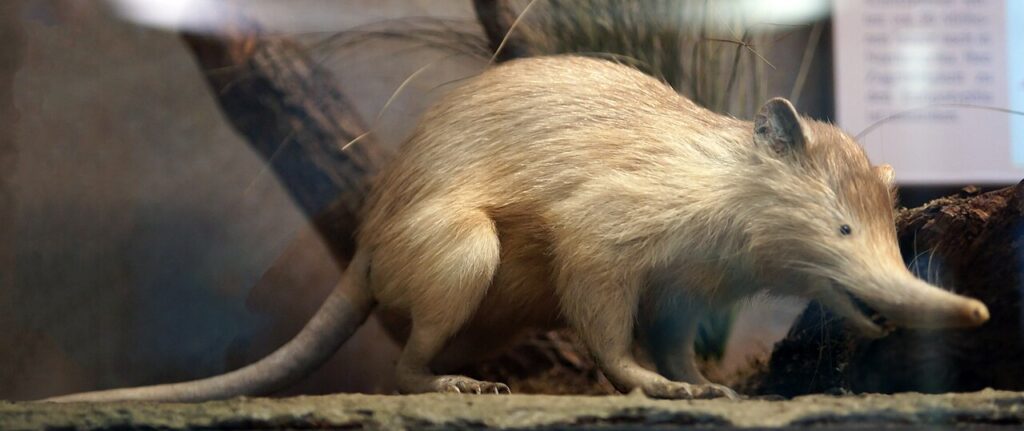

The solenodon is an ancient, nocturnal mammal that has remained largely unchanged for millions of years. Native to the Caribbean, this small, rat-like creature is one of the only surviving species of an ancient group of mammals that once roamed the Earth. The solenodon is unique in that it has retained many primitive traits that were lost in other mammalian lineages, making it a living fossil.
Despite its fascinating history, the solenodon is critically endangered due to habitat loss and predation by non-native animals. Its nocturnal habits and unique biology have made it a subject of interest for scientists studying evolution and the persistence of ancient species.
Pink Fairy Armadillo
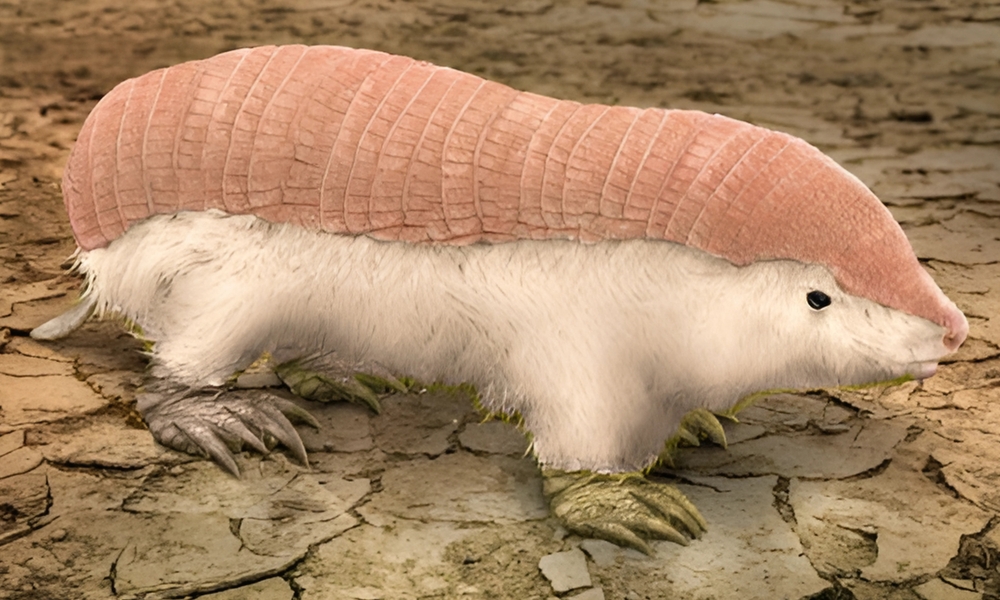
The pink fairy armadillo is a small, nocturnal mammal found in Argentina. This unique creature has a soft, pinkish shell that covers its back, giving it a distinct appearance compared to other armadillos. It is the smallest species of armadillo, and unlike other armadillos, it has a highly flexible, leathery shell that allows it to burrow deep into the sandy soil of the Argentinean deserts. Its large, sharp claws are perfectly designed for digging, and its speed and agility make it a quick and elusive creature.
Despite its adorable appearance, the pink fairy armadillo is difficult to spot in the wild due to its nocturnal habits and remote habitat. It faces threats from habitat destruction and predation by non-native species, and is rarely seen in the wild. Its strange, delicate appearance, combined with its impressive digging abilities, makes it an animal that sparks curiosity and wonder.
Vampire Bat
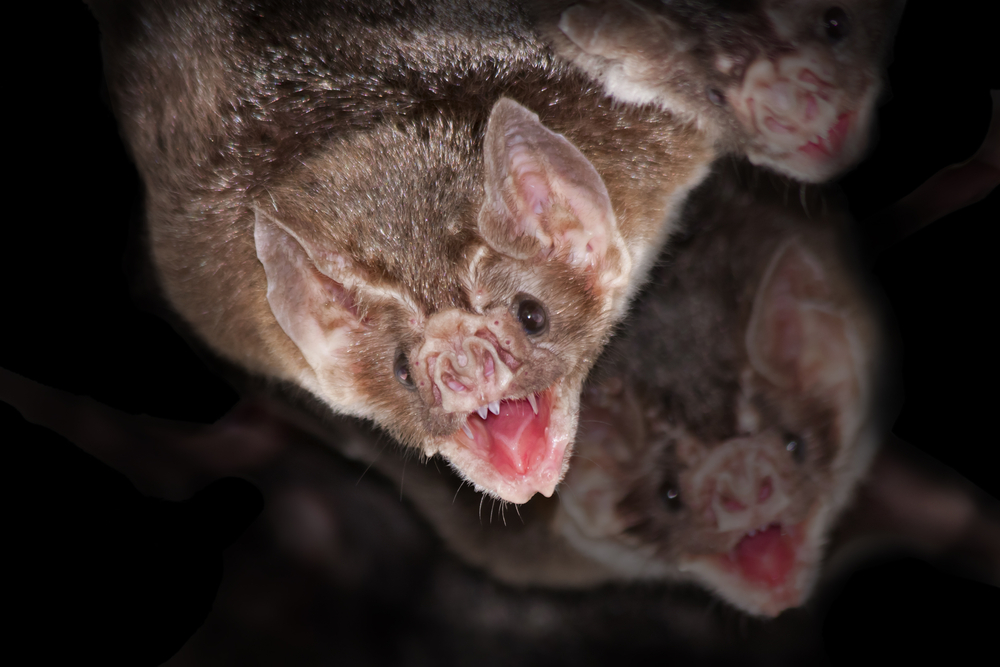

Vampire bats are the stuff of legends, but these real-life creatures have fascinated humans for centuries. Native to Latin America, these small, nocturnal mammals feed on the blood of other animals, including livestock and even humans. What makes them particularly intriguing is the way they drink blood: using their sharp teeth, they make a small incision in their prey’s skin and lap up the blood that flows out. To ensure that their prey does not wake up, vampire bats secrete an anticoagulant in their saliva that keeps the blood flowing freely.
Though their feeding habits may seem gruesome, vampire bats play an important role in their ecosystem by controlling insect populations. Their ability to find prey in the dark using sophisticated heat sensors is a remarkable adaptation to their nocturnal lifestyle. Despite their spooky reputation, these creatures are often misunderstood, and their unique feeding behavior continues to captivate researchers.
This article originally appeared on Avocadu.
