11 Historic Events That Influenced the Evolution of Georgian Furniture
Georgian furniture emerged during the early 18th century and is renowned for its balance between beauty and function. The style includes elegant lines, ornate carvings, and high-quality materials, reflecting the tastes of the period. Key historical events during the Georgian era had a profound impact on furniture design and production. These events influenced everything from the materials used to the types of furniture that became popular. Let us take a closer look at the major milestones that shaped the evolution of this classic style.
This post may contain affiliate links, which helps keep this content free. Please read our disclosure for more info.
The Reign of George I (1714-1727)

The early Georgian period began with the ascension of George I in 1714. His reign marked the start of the Hanoverian dynasty and brought about changes in British society, including a growing middle class. During this time, furniture design began to shift toward more refined and symmetrical shapes, moving away from the more elaborate Baroque style. The shift towards simplicity allowed for the development of new techniques and the use of new materials in furniture making.
Furniture makers began focusing more on comfort and functionality, alongside aesthetic beauty. The influence of Dutch and French design styles can be seen in early Georgian pieces. The introduction of walnut wood became popular, as it was both durable and beautifully rich in color. The Georgian style gradually evolved to reflect the elegance and sophistication of the early 18th century.
The Rise of the British Empire
The expansion of the British Empire in the 18th century had a profound impact on furniture design. The growing wealth from trade and colonial expansion allowed for more lavish designs in British homes. New materials, such as exotic woods and fabrics, became available, influencing furniture styles. Furniture makers were now able to incorporate luxurious elements from around the world, making their pieces highly desirable.
As the empire expanded, so did the demand for high-quality furniture, and this period saw an increase in the production of fine craftsmanship. The use of mahogany, a wood imported from the Caribbean, became a hallmark of Georgian furniture. The wealth and cultural exchange driven by the empire shaped both the design and material choices of furniture makers. This era of growth and exploration introduced elements of international influence into the domestic interiors.
The Industrial Revolution (Late 18th Century)
The Industrial Revolution brought about dramatic changes in manufacturing techniques, particularly in the furniture industry. The rise of factories and mechanized production allowed for the mass production of furniture, making it more accessible to a wider audience. While craftsmanship still played a key role, machines began to take over many aspects of production, reducing the labor required for intricate details. This shift allowed furniture to become more affordable while still maintaining an air of sophistication.
The introduction of new technologies and machinery, such as steam engines, made it easier to produce furniture in larger quantities. As a result, furniture design became more standardized, but still incorporated the refined elements of the Georgian style. While the individual artistry of furniture makers was impacted, the quality and variety of furniture available to the public increased. The Industrial Revolution thus played a crucial role in making Georgian-inspired furniture accessible to more people.
The Neoclassical Movement (Mid to Late 18th Century)

The Neoclassical movement, which began in the mid-18th century, had a major influence on Georgian furniture. This movement was inspired by the classical art and architecture of ancient Greece and Rome. It emphasized simplicity, symmetry, and the use of straight lines, which led to the development of more restrained and refined designs. Furniture began to feature classical motifs, such as fluted columns, urns, and laurel wreaths, reflecting the aesthetic ideals of the time.
Neoclassical furniture was often made with lighter, more delicate proportions than the earlier Baroque-inspired pieces. The use of lighter woods, such as satinwood, became more prevalent, and designs often incorporated inlaid patterns and decorative carvings. This period marked a departure from the heavy, ornamental style of earlier decades, ushering in a new era of elegance and grace. The Neoclassical influence brought a sense of order and refinement to Georgian furniture, shaping its design for the future.
The Georgian Fashion for Chinoiserie (Early to Mid 18th Century)

The fashion for Chinoiserie, the European interpretation of Chinese and East Asian decorative arts, became a key influence during the Georgian era. As trade with China and other parts of Asia grew, exotic patterns and designs began to influence British furniture. This resulted in the incorporation of elements like lacquer, intricate floral patterns, and asymmetrical designs into furniture. Chinoiserie became especially popular during the reign of George II and remained influential for much of the 18th century.
Furniture makers began creating pieces with painted and lacquered surfaces inspired by Chinese art. The use of bright colors and intricate details became common in both the design and decoration of furniture. Chinoiserie also led to the use of new materials such as lacquered wood and silk. The incorporation of these exotic elements helped distinguish Georgian furniture and added a unique flair to the pieces of the time.
The French Influence (Late 17th to 18th Century)

French design had a lasting impact on Georgian furniture, especially during the reigns of George I and George II. French styles, particularly Rococo and later Louis XVI, brought intricate carvings, delicate shapes, and luxurious materials into British interiors. This French influence contributed to the increased use of gilt and inlaid patterns, as well as the refinement of shapes, making furniture more decorative and ornate.
French furniture design also encouraged the use of upholstery and fabrics, making comfort a higher priority in furniture production. The influence of French artisans and their techniques shaped the development of Georgian furniture, creating a more opulent and detailed aesthetic. French craftsmanship and design principles were closely followed by British furniture makers, and many of the finest Georgian pieces are a direct reflection of these influences. The French style remains an integral part of Georgian furniture history.
The Invention of the Windsor Chair (Mid 18th Century)
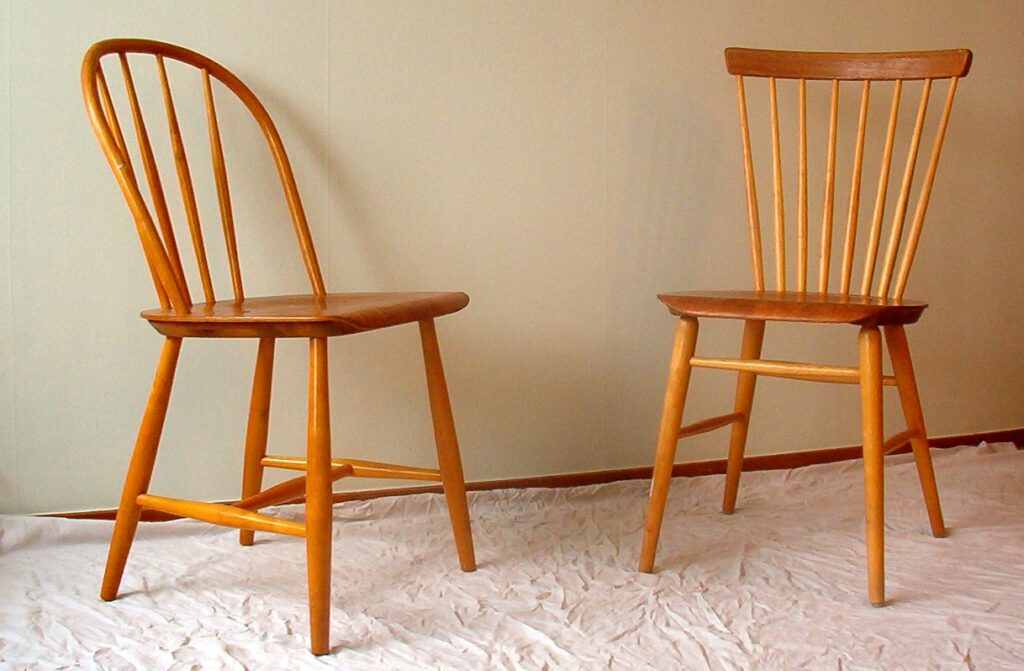

The Windsor chair, invented in the mid-18th century, quickly became a staple in Georgian furniture. This iconic chair design combined elegance with practicality, featuring a distinctive curved back and spindles. Originally made from beech or elm, the Windsor chair became popular in both formal and casual settings due to its comfort and durability. Its design was simple yet effective, making it a versatile piece that fit into many types of homes.
The Windsor chair’s influence extended beyond just practical seating; it became a symbol of Georgian craftsmanship and was widely adopted across Britain. Its distinctive form was ideal for both dining rooms and living spaces, contributing to its widespread use. The success of the Windsor chair encouraged the production of similar designs in various forms, solidifying its place in the history of Georgian furniture. It remains one of the most recognizable pieces from the period.
The Grand Tour and the Rise of Collecting (18th Century)
The Grand Tour, a traditional trip across Europe undertaken by young British men in the 18th century, had a significant impact on the evolution of Georgian furniture. As wealthy travelers collected art, antiques, and furniture from across Europe, their tastes began to influence British interior design. The items they brought back from their travels often featured classical and continental designs, which were incorporated into Georgian furniture.
The fascination with foreign cultures and art led to the incorporation of European and even Asian influences into British furniture. This period saw the rise of collecting as a hobby among the British elite, with furniture serving as a symbol of wealth and sophistication. The Grand Tour expanded the horizons of Georgian furniture design, encouraging the fusion of different cultural elements into new and exciting pieces. The impact of these travels can still be seen in many Georgian furniture styles today.
The Regency Era and the Influence of George IV (1811-1830)
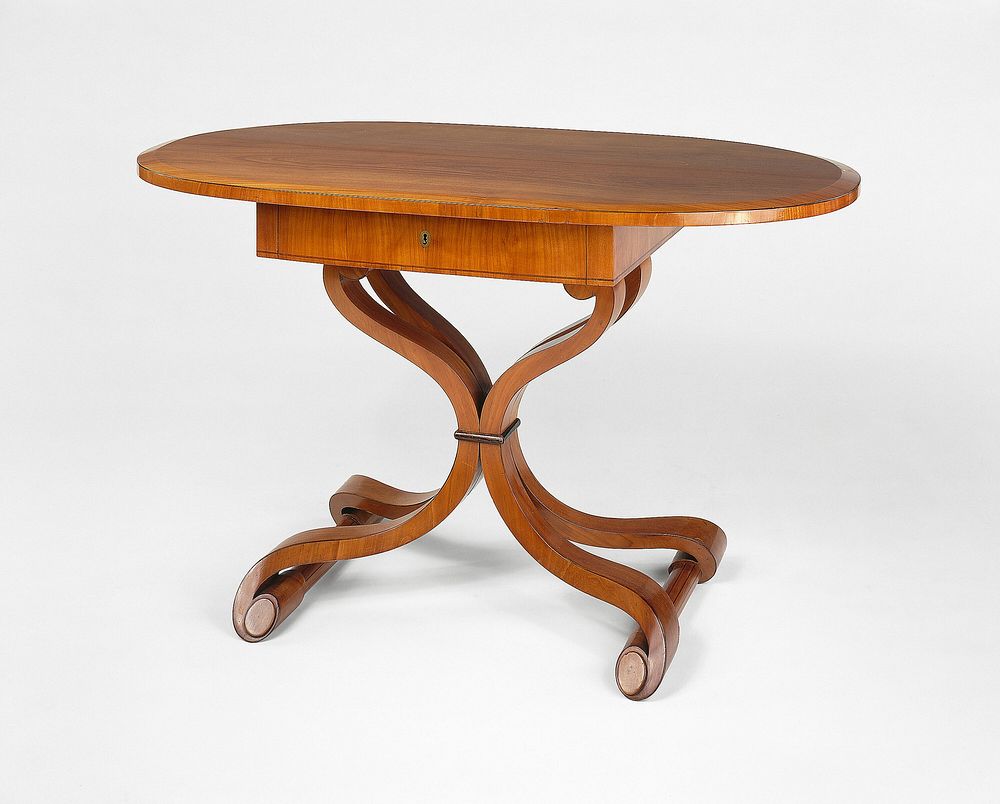

The Regency era, under the rule of George IV, introduced significant shifts in both style and design. During this time, furniture became even more refined and luxurious, influenced by French Empire and Neoclassical styles. This period saw the introduction of lavish materials like mahogany and the use of intricate inlay work. The designs of this era were characterized by bold, geometric shapes and the integration of classical elements such as fluted columns and lion’s feet.
The Regency style became a symbol of wealth and social status, and furniture makers embraced the trends of the time. Many famous designers, such as Thomas Hope and George Smith, shaped the direction of Regency furniture. The influence of George IV’s reign helped elevate furniture design to new heights, combining elegance with opulence. Regency-era furniture is now highly valued by collectors and remains an iconic part of Georgian furniture history.
The Victorian Era (1837-1901)
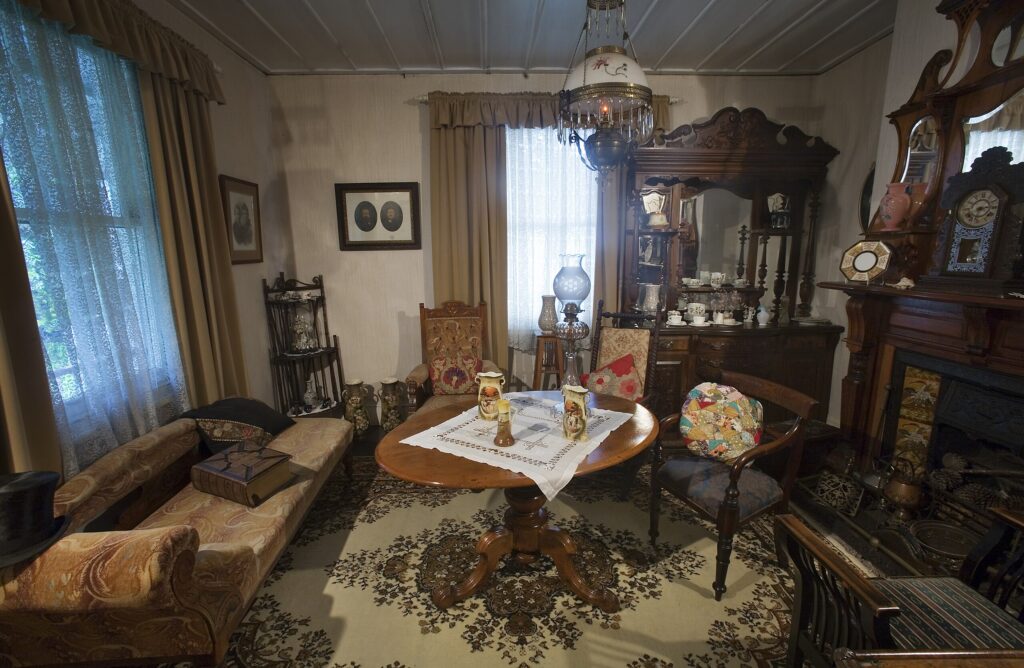

The Victorian era, while slightly outside the Georgian period, still drew heavily from the designs of the 18th century. The era’s interest in historical revivalism meant that Georgian-inspired furniture saw a resurgence, with intricate carvings and ornate details becoming fashionable again. The Victorians embraced heavy, dark woods like oak and mahogany, often with highly decorative elements. This period saw the blending of Georgian styles with newer, more ornate designs, contributing to the long-lasting influence of Georgian furniture.
Victorian furniture often featured elaborate upholstery, brass accents, and dark wood finishes, taking inspiration from earlier Georgian pieces. The mass production of furniture during this time made it widely available to the growing middle class. While Victorian furniture was often more elaborate than traditional Georgian styles, the foundation of design remained rooted in earlier eras. The Victorian period played a role in continuing the legacy of Georgian furniture into the 19th century.
The Introduction of the Cabinetmaker’s Guild (18th Century)

The establishment of the Cabinetmaker’s Guild in the 18th century brought about significant advancements in furniture production. The guilds were responsible for setting high standards for craftsmanship and ensuring quality control in furniture making. As a result, the design of Georgian furniture became more sophisticated, with highly skilled artisans producing finely detailed pieces. The establishment of these guilds helped establish furniture-making as a respected profession, influencing the industry for generations.
Guilds ensured that only the most talented craftsmen were able to produce furniture, leading to more refined and intricate designs. The rise of the Cabinetmaker’s Guild also helped standardize the construction of furniture, making it more consistent. With these high standards in place, Georgian furniture became a symbol of both wealth and artistry. The legacy of these guilds can still be seen in the quality and detail of Georgian furniture today.
The evolution of Georgian furniture is a testament to the cultural and historical shifts that took place during its time. These influential events not only changed the design and materials used but also the way furniture was perceived and valued.
This article originally appeared on Avocadu.
